Fisher-Yate洗牌算法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
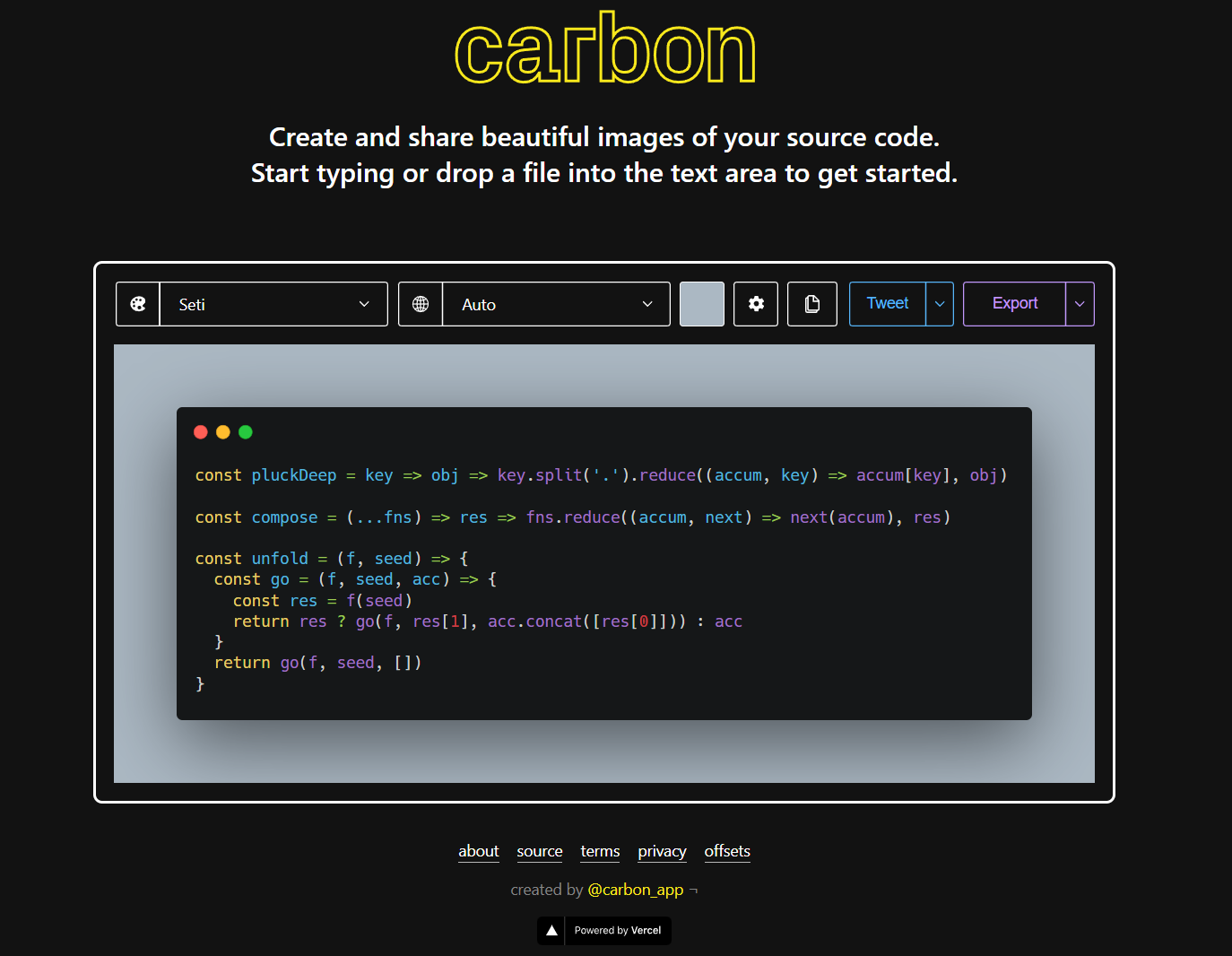
| function shuffleArray(array) {
for (let i = array.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
const j = Math.floor(Math.random() * (i + 1));
[array[i], array[j]] = [array[j], array[i]];
}
return array;
}
|
这个 shuffleArray 函数接受一个数组作为参数,并返回打乱顺序后的新数组。它使用了 Fisher-Yates 洗牌算法的思想:
- 从最后一个元素开始,向前遍历数组。
- 对于每个元素,生成一个随机索引 j,范围是从 0 到当前元素的索引 i。
- 将当前元素与随机索引 j 处的元素交换位置,通过解构赋值实现。
- 继续向前遍历数组,直到遍历完所有元素。
- 返回打乱顺序后的数组。
使用示例:
1
2
3
4
| const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const shuffledArray = shuffleArray(array);
console.log(shuffledArray);
|
这将输出一个随机打乱顺序的数组,例如 [3, 1, 5, 2, 4]。每次运行结果都可能不同,因为数组的顺序是随机的。
分开打乱(前面的多少个在里面打乱和后面部分里面打乱)
示例:前面6个在这6个里面打乱,后面的在后面里面打乱
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| function shuffleArray(array) {
const firstFive = array.slice(0, 6);
const remaining = array.slice(6);
for (let i = firstFive.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
const j = Math.floor(Math.random() * (i + 1));
[firstFive[i], firstFive[j]] = [firstFive[j], firstFive[i]];
}
for (let i = remaining.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
const j = Math.floor(Math.random() * (i + 1));
[remaining[i], remaining[j]] = [remaining[j], remaining[i]];
}
return firstFive.concat(remaining);
}
|